Introduction
Melanoma, a severe form of skin cancer, has been notoriously challenging to treat. A recent breakthrough in melanoma treatment, published in Nature Nanotechnology, explores the potential of using tyrosine, an amino acid, to target melanoma cells effectively. This innovative approach combines nutrient delivery with advanced therapeutic techniques to inhibit tumor growth and enhance treatment efficacy.
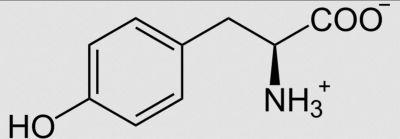
Role of Tyrosine in Melanoma
Tyrosine is essential for melanin production in melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation in the skin. Melanoma cells, which originate from melanocytes, rely heavily on glycolysis, a process that provides them with the energy required for rapid growth. By manipulating tyrosine metabolism, researchers can disrupt this energy production pathway, hindering the proliferation of melanoma cells.
Innovative Approach for Melanoma Treatment
The study introduces l-Tyrosine–oleylamine nanomicelles (MTyr–OANPs), a novel method to deliver tyrosine directly to melanoma cells. These nanomicelles penetrate the cells and reactivate melanogenesis, the process of melanin production. Reactivating melanogenesis interferes with glycolysis, effectively starving the cancer cells of their primary energy source.
Enhanced Photothermal Therapy
In addition to disrupting glycolysis, the MTyr–OANPs were used in combination with photothermal therapy. Photothermal therapy involves using heat to destroy cancer cells. The study found that the combined treatment significantly improved therapeutic outcomes. In experiments with melanoma-bearing mice, the tumors were effectively eradicated, demonstrating the potential of this combined approach.
Benefits of the Treatment
The benefits of this new treatment method are substantial. By specifically targeting melanoma cells, the treatment minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues. The inhibition of glycolysis starves the cancer cells, slowing their growth and spread. Furthermore, the enhanced photothermal therapy offers a non-invasive treatment option that can be used alongside existing therapies to improve overall effectiveness.
Future Implications
This research suggests that targeting specific metabolic pathways with nutrients like tyrosine could revolutionize cancer treatment. The promising results from this study pave the way for further research and development of nutrient-based therapies. As we continue to explore and understand the metabolic dependencies of cancer cells, innovative treatments like this could significantly improve patient outcomes and offer new hope in the fight against melanoma.
Conclusion
The study published in Nature Nanotechnology provides a groundbreaking approach to melanoma treatment by leveraging the metabolic requirements of cancer cells. By using tyrosine to inhibit glycolysis and enhance photothermal therapy, researchers have developed a promising strategy to combat this aggressive form of skin cancer. This innovative approach opens new avenues for cancer treatment and highlights the potential of targeting metabolic pathways in cancer therapy. For more details, you can read the full study here.
